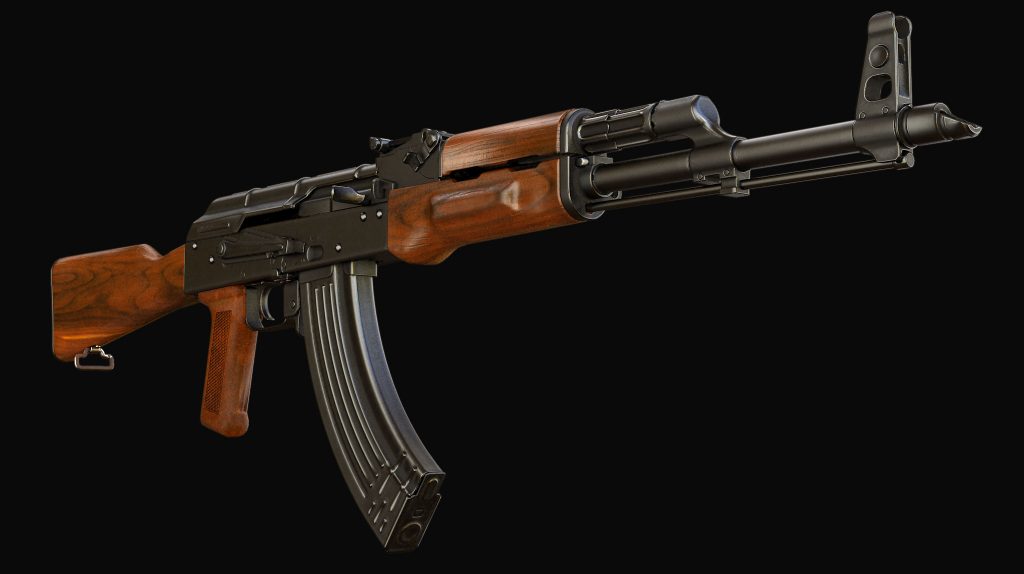
Kalashnikov Modernized assault rifle (AK, AKM, AK-47) – The world’s most widespread and reliable weapon
Kalashnikov Modernized assault rifle
Specifications
Barrel caliber – 7.62 mm, original cartridge – type 7.62×39 (version of 1943), total weight, empty – 3.1 kg, rifle length w/o bayonet – 0.88 m, total length of the entire barrel – 0.415 m, muzzle velocity – 715 m/s, maximum rate of fire – 660 shots/min, maximum combat velocity – 40/100 shots per minute, maximum firing range – 1,000 m, original magazine capacity – 30 rounds.
Operating principle
The assault rifle automatic principle of operation relies on application of powder gases that release the energy needed to reload. When a shot is made the released powder gases get into a dedicated gas tube wherein an original piston pulls back the bolt and reloads the weapon.
The recoil spring guide assembly and a dedicated bolt carrier move to the foremost position. This motion helps a cartridge to get into a special breech chamber, locking the bore. The custom-designed bolt carrier enables the trigger to be released automatically.
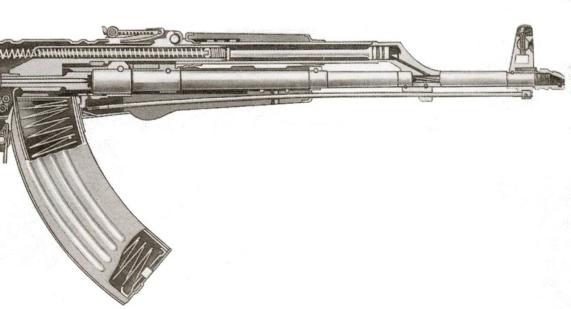 The automatic system in AK assault rifle uses the energy of powder gases vented via the hole in the barrel side
The automatic system in AK assault rifle uses the energy of powder gases vented via the hole in the barrel side
Development
The availability original automatic and self-loading weapons in the armed forced was in focus in the Soviet Union in early 20th century. Automatic rifles that fully replaced the renowned 3-line rifle in the pre-war period appeared to be most promising in terms of efficiency and functionality. By 1940, the Soviet Army had in its arsenals Simonov automatic rifle (AVS-36) and Tokarev self-loading rifle (SVT-38). Both models proved their worth in combat, enabled to reveal their advantages and flaws. Priority was given to the model with automatic reloading feature. The military leaders subsequently adopted the SVT rifle, with slight modifications and improvements to the SVT-40 model.

In early 1943, Soviet inventors released a 7.62 mm cartridge. The cartridge power met the applicable requirements in place for contemporary weapons.
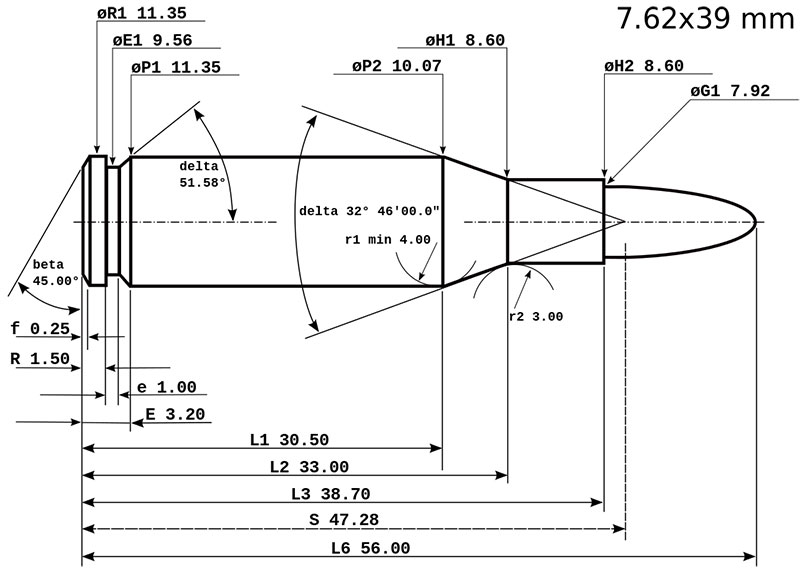
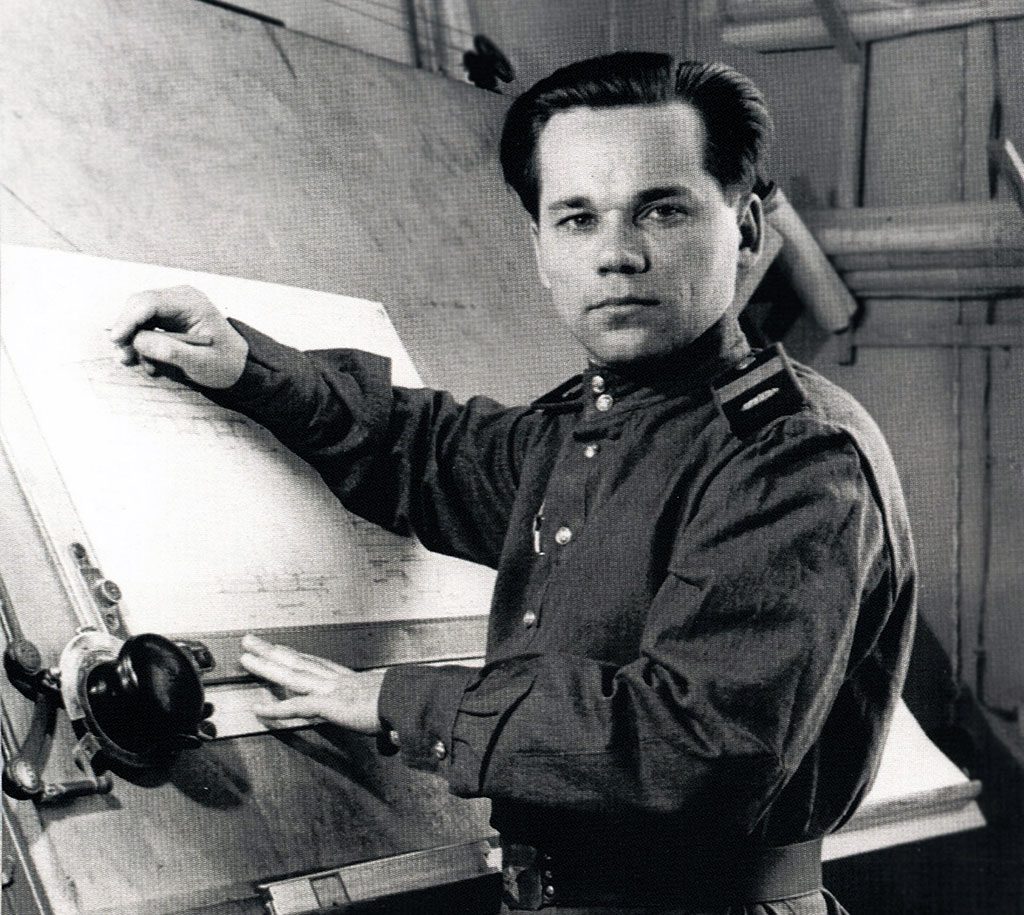
Further on, a whole line of weapons that would be able to exceed the technical parameters of the renowned Mosin rifle and Shpagin’s PPSh-41 submachine gun was developed and designed for this cartridge.
The meticulous development of a totally new model known as the “assault rifle” was launched in 1944. The simultaneous development efforts brought together several design bureaus, with professional skills in this manufacturing field. All the work related to the assault rifle design were personally supervised by Simonov, Degtyaryov, Sudaev, and many other gunsmiths of the time.
Tender
In early 1945, the Main Artillery Directorate that acted as the core customer in terms of domestic weapons for army needs announced a special tender for development of a new assault rifle type for the new rifle cartridge. The major conditions for design included best possible accuracy of fire, small dimensions of the weapon, reliability under heavy use, durability and endurance to various modes of combat. M. Kalashnikov, a young designer employed by a military scientific center, joined the work on designing the future assault rifle prototype in 1946.

Two main bidders were announced: SKS self-loading carbine by Simonov and Kalashnikov assault rifle, the latter to be adopted by the Soviet Army from 1949 as AK-47. The assault rifle design features enabled to spend much less time and money to manufacture this weapon model. That feature immediately ousted Simonov’s carbine to the sidelines as a more complicated item in manufacture.
Origin of the legend
The Kalashnikov assault rifle had smaller dimensions that ensured required degree of comfort in combat operations. The ability to fire single shots or bursts drastically expanded the weapon’s potential application.

As a version has it, designer Kalashnikov borrowed the configuration of his assault rifle by copying a German weapons model. German МР 43 assault rifle has similar outlines and internals, but a detailed examination reveals a drastic difference in the concepts of those two weapon types. Differing systems for barrel locking, cartridge feeding and distinct trigger and firing mechanism entirely dispel that myth.

Most carefully merged existing research results in a single project became the major achievement of the entire Kalashnikov-led team of professionals engaged in designing and manufacturing of the new assault rifle model. The work enabled to give birth to a unique weapon that fully met all the requirements and conditions the designers needed to fulfill.

Some components of the original assault rifle were initially made of poor-quality materials to reduce the cost of production. However, continuous improvement of the weapon began as it was gaining popularity and demand.
In 1959, a regular upgrade was implemented to improve the strength of the original receiver. This modification of the original assault rifle was called Modernized Kalashnikov assault rifle (AKM). The upgrades essentially enhanced the strength of the unique receiver, and drastically curtailed the assault rifle manufacturing cost.
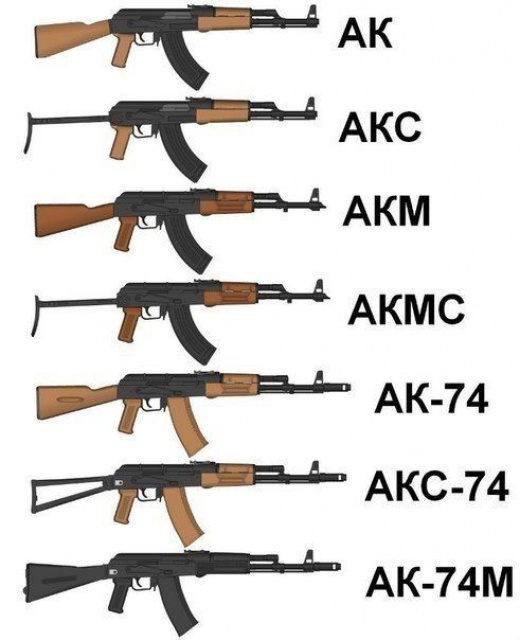

The modernized АКМ rifle stood apart from its earlier versions for its increased shooting range, reinforced receiver, upgraded butt stock, a dedicated hammer retarder, improved durability indicators in horizontal position, a special muzzle brake and addition of a removable bayonet suitable for various purposes.
Use
Following its triumphant march in the global arena, AKM was often delivered to countries that supported the policies of the USSR. Sometimes, instead of delivering a definite number of weapons the USSR would grant to its allies licenses to manufacture the Kalashnikov assault rifle, along with the required engineering documentation.

In the Soviet era, nearly every school student could assemble the Kalashnikov assault rifle in its contemporary modifications. Therefore, the young men enlisted to military service received in their hands the weapons they already knew.
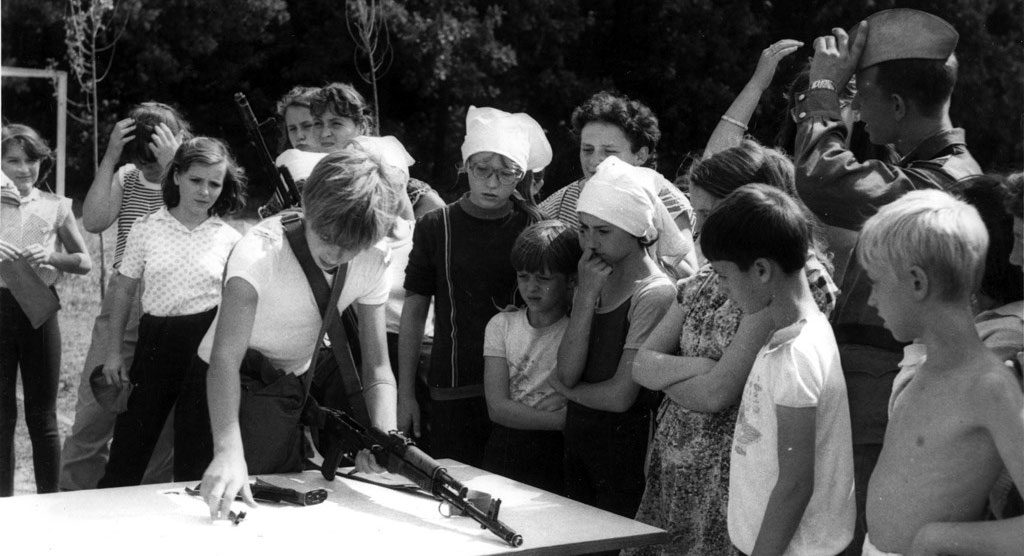

To date, more than 90 million of the Kalashnikov assault rifles were manufactured globally.
Various modifications of the assault rifle have been used for civil purposes. Such weapon models are widely used in many countries due to their outstanding performance parameters.

Highest reliability in use in the toughest environments, low required level of maintenance, simplicity of design and affordable production cost are the most evident advantages of the Kalashnikov assault rifle.
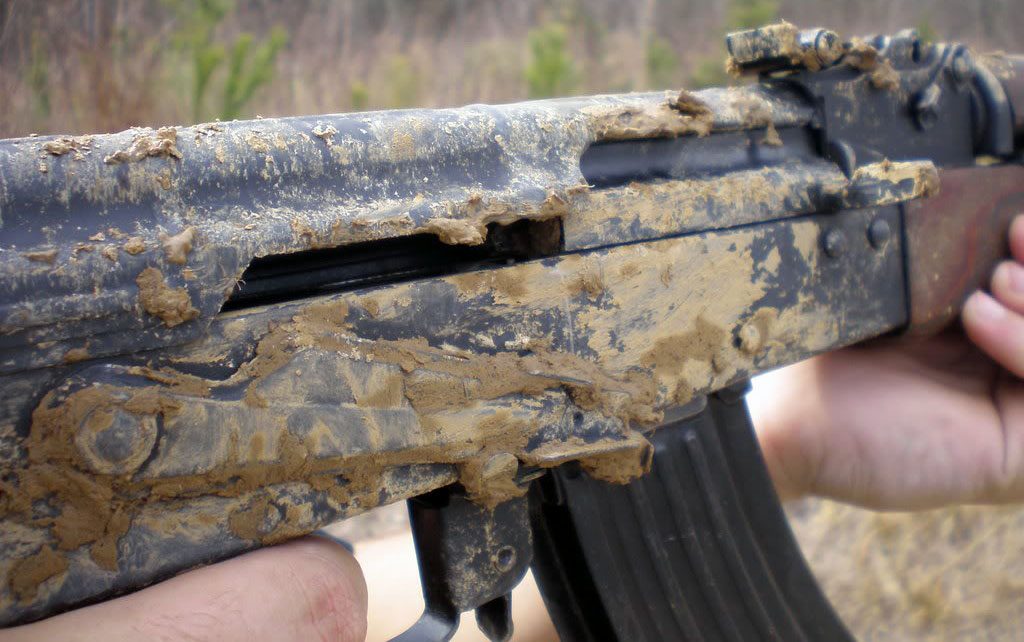

Some enthusiasts even successfully held an underwater shooting experiment.
Nowadays, Kalashnikov assault rifle is included in the Guinness Book of World Records as the most widespread small arms model around the world.
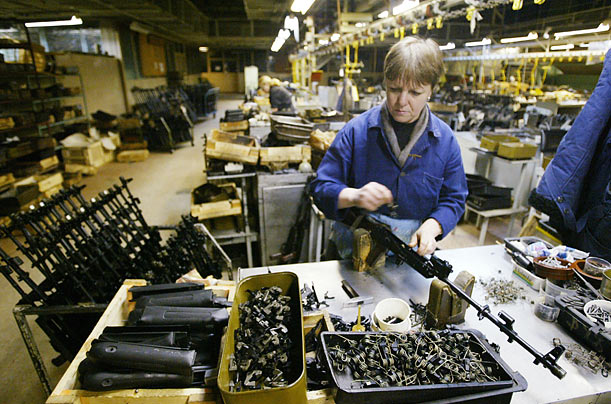 All modifications and original models of the Kalashnikov assault rifle account for more than 15% of the total number of small arms across the globe.
All modifications and original models of the Kalashnikov assault rifle account for more than 15% of the total number of small arms across the globe.
